How to Open Activity Monitor Using Terminal on Mac
In macOS, Activity Monitor is a powerful tool that provides insight into the performance and resource usage of your computer. While you can easily access it through the Finder or Launchpad, you might prefer using Terminal for a faster and more streamlined approach.
In this blog post, we’ll guide you through the process of opening Activity Monitor on Mac from the Terminal. Follow the steps given below.
- Open Terminal The first step is to open Terminal. You can find it in the Utilities folder within the Applications folder. Alternatively, you can search for it using Spotlight by pressing Cmd+Space and typing Terminal.
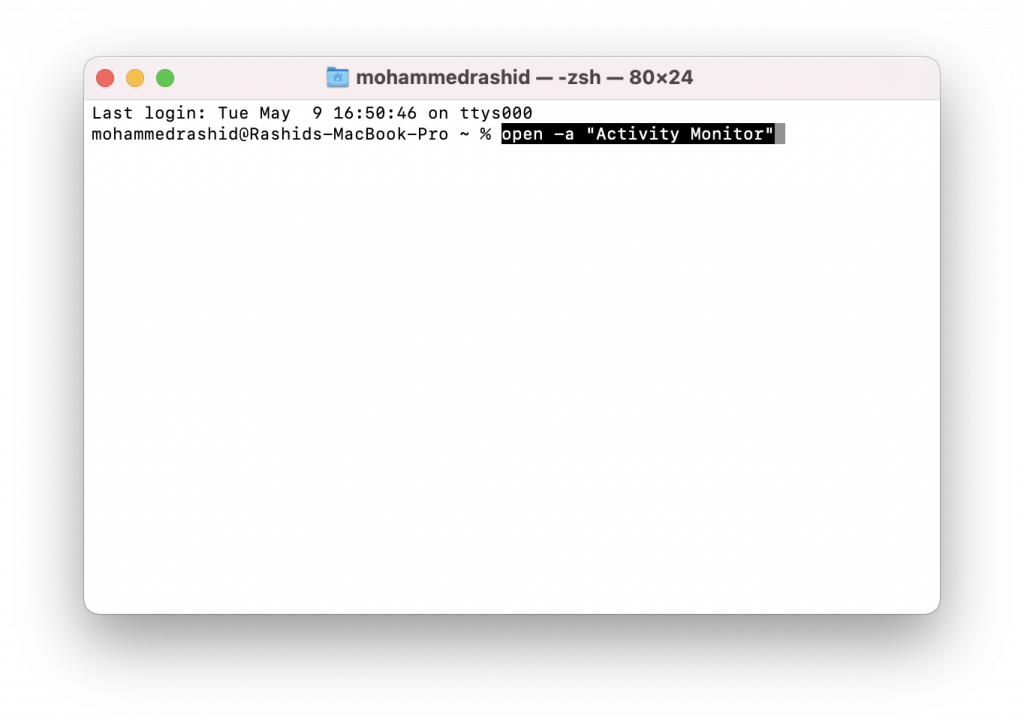
- Once the Terminal is open, you’ll need to enter the following command:
open -a "Activity Monitor"
This command tells the Terminal to open the Activity Monitor application. After typing the command, press Enter.
- Access Activity Monitor Following the command execution, Activity Monitor will open in a new window. Now, you can monitor your Mac’s CPU, memory, energy, disk, and network usage.
Using Terminal Commands to Monitor System Performance Apart from opening Activity Monitor through Terminal, you can also use various Terminal commands to monitor your Mac’s performance directly.
Some useful commands include:
- top: This command displays the list of processes and their resource usage, similar to Activity Monitor’s CPU tab. Type
topand press Enter to execute the command. To exit the ‘top’ view, press ‘q’. - vm_stat: This command provides information about your Mac’s virtual memory usage. To execute the command, type
vm_statand press Enter. - iostat: The iostat command shows the input/output statistics for your Mac’s disks. To execute the command, type
iostatand press Enter. - netstat: Use this command to display information about your Mac’s network connections. Type
netstatand press Enter to execute the command. - sysctl: This command can be used to retrieve various system statistics, such as the total amount of RAM. Type
sysctl hw.memsizeand press Enter to view your Mac’s total memory size in bytes.
Opening Activity Monitor from Terminal is a quick and efficient method for users who prefer working with command-line interfaces.
Additionally, Terminal offers numerous commands that allow you to monitor your Mac’s performance directly. Familiarizing yourself with these commands can help you optimize your system and maintain its health.




